Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Improvement in Age at Mortality and Changes in Causes of Death in the Population with Diabetes: An Analysis of Data from the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
- Eugene Han, Sun Ok Song, Hye Soon Kim, Kang Ju Son, Sun Ha Jee, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(3):466-474. Published online June 29, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1440
- 3,909 View
- 138 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Diabetes is a leading cause of death that is responsible for 1.6 million annual deaths worldwide. However, the life expectancy and age at death of people with diabetes have been a matter of debate.
Methods
The National Health Insurance Service claims database, merged with death records from the National Statistical Information Service in Korea from 2006 to 2018, was analyzed.
Results
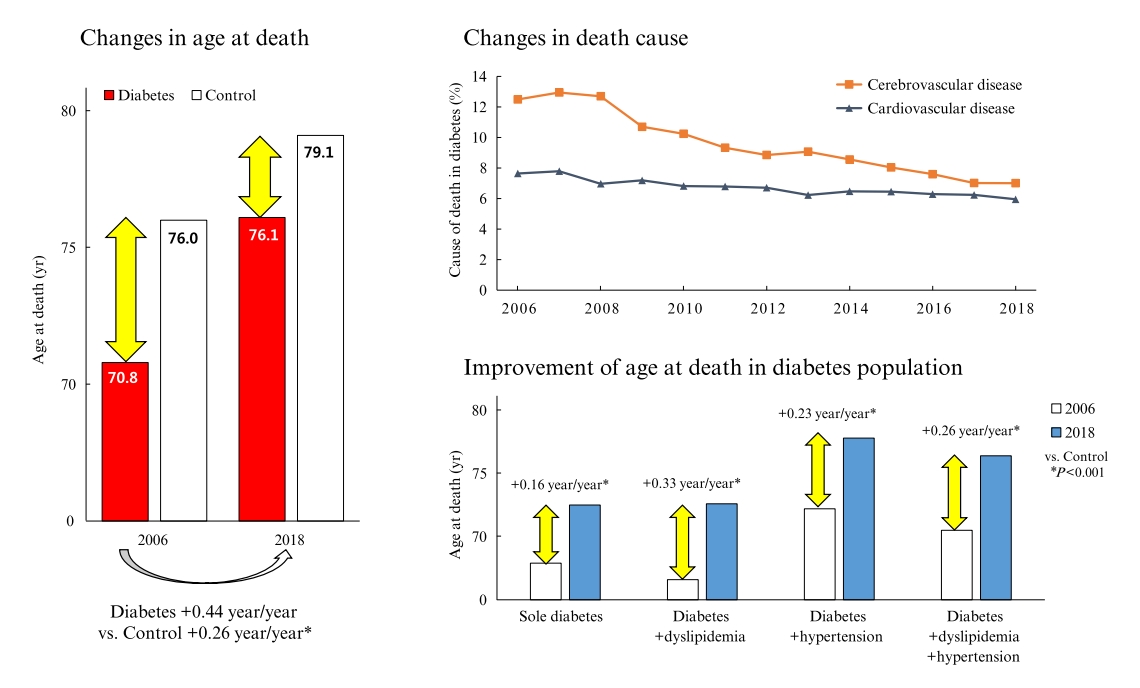
In total, 1,432,567 deaths were collected. The overall age at death increased by 0.44 and 0.26 year/year in the diabetes and control populations, respectively. The disparity in the mean age at death between the diabetes and control populations narrowed from 5.2 years in 2006 to 3.0 years in 2018 (p<0.001). In a subgroup analysis according to the presence of comorbid diseases, the number and proportion of deaths remained steady in the group with diabetes only, but steadily increased in the groups with diabetes combined with dyslipidemia and/or hypertension. Compared to the control population, the increase in the mean death age was higher in the population with diabetes. This trend was more prominent in the groups with dyslipidemia and/or hypertension than in the diabetes only group. Deaths from vascular disease and diabetes decreased, whereas deaths from cancer and pneumonia increased. The decline in the proportion of deaths from vascular disease was greater in the diabetes groups with hypertension and/or dyslipidemia than in the control population.
Conclusion
The age at death in the population with diabetes increased more steeply and reached a comparable level to those without diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Cause-of-Death Mortality in Children and Young Adults with Diabetes: A Nationwide 10-Year Follow-Up Cohort Study
Iee-Ho Choi, Sang-Woo Yeom, Sun-Young Kim, Jihye You, Jong-Seung Kim, Minsun Kim
Children.2023; 10(2): 358. CrossRef - Age at Mortality in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Who Underwent Kidney Transplantation: An Analysis of Data from the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Sun Ok Song, Eugene Han, Kang Ju Son, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(9): 3160. CrossRef - Risk of Cause-Specific Mortality across Glucose Spectrum in Elderly People: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Joonyub Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Soon Jib Yoo, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 525. CrossRef - Long-Term Cumulative Exposure to High γ-Glutamyl Transferase Levels and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Han-Sang Baek, Bongseong Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Sang-Ah Chang, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Seung Yun
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 770. CrossRef
- Analysis of Cause-of-Death Mortality in Children and Young Adults with Diabetes: A Nationwide 10-Year Follow-Up Cohort Study


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



